E-commerce trends 2023
Table of contents
Internationalisation and Glocalization
Another important trend that fashion brands should keep in mind in 2023 is the internationalisation and localisation of e-commerce. The international expansion of e-commerce for fashion brands is more and more important to ensure the continuous growth in terms of sales of digital channels.
The problems that happened with some current important markets for global fashion brands, such as Russia and China, put pressure on fashion houses to find new markets for their products.
For example in the Middle Eastern countries that are part of the Gulf corporation, such as the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Qatar and Jordan are now becoming relevant markets for DTC e-commerce.
In order to reach these countries with Direct to Consumer e-commerce, fashion brands need to structure their teams and their e-commerce divisions with the ability to invoice local customers, create transport and sales documents for customs, localise their websites in several languages, provide customer service in local languages, implement payment methods that are suitable and widely available in these countries and finally to have the support of a logistic structure that is able to deliver orders on time and according to the needs of the local customers. For example the delivery company may need to support the acquisition of cash from the customers in case of cash on delivery payment.
Fashion brands have few options to implement this type of e-commerce services
- The first option is to ship cross-border from the home country of the brand, for example a brand could ship from Italy to KSA;
- The second option is to create a local e-commerce team in the destination country,
- The third option would be to use the services provided by companies that are specialised in enabling cross border e-commerce for fashion brands.
- Go-direct option
The first option which may seem the least expensive for fashion brands may lead to results below the expectations. This could happen for example because the brand is not able to implement the payment systems that are required to be successful in the destination market, or because the customer service is not able to satisfy the requests of the local clients. For example if you are selling from Europe to the United States and the customer service is based in Europe and operates only at European working hours, which means that the customer service based in Europe is not able to meet the real time demands of the American customers due to the time difference.
- Local team creation
If you decide to set up a local team in the destination country you will incur in fixed costs that will need to be balanced with the revenues that the e-commerce is able to generate. In this case the classic functions of e-commerce which are strategic Direction, Digital Marketing, E-commerce Operations, Information Technology, Merchandising and Store Management, need to be executed by the local team. Therefore the minimum size of a local team for a fashion brand is around 3 to 5 people. So if the estimated revenues for the e-commerce channel are higher than the fixed cost of a team of 3 to 5 people, plus the variable costs associated with the running of the e-commerce, the local team creation could be the right solution for your brand.
- Service providers
The third option for fashion companies is to use specialised service providers who have the capabilities to deliver the services you need to meet the local customers expectations for a price, which is generally a commission fee to pay on the net sales. The advantage of using service providers is connected with both the time to market and and the absence of fixed costs. The downside of working with service providers is that you need to give up part of your revenues to pay the commissions for the services.
The artificial intelligence trend in e-commerce
One of the biggest e-commerce trends in terms of technological enhancements is artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence applications, that up until few years ago were restricted to laboratory or simple research projects, are now coming out of the laboratory and finding real application in the fashion business.
An example of this application is artificial intelligence for customer service, even if we’re not 100% there yet we’re getting quite close to having AI assistants to be able to provide potential customers with answers about product availability, product price, fit and other information. On the other hand we can also use artificial intelligence assistance to help human people employed in customer services offices to expedite their functions of retrieving information about products.
But AI is not just applications that we need to install and configure, we use AI features everyday in our email systems or in our marketing activities without knowing it or without being aware of it. The whole Google marketing suite starting from Google ads has progressively moved from human intervention to a black box approach based on machine learning where we feed Google some inputs: assets; our budget and our our goals, and Google create and consequently optimise the adverts to perform according to our let’s say expectations.
If you think of natural language processing or NLP which is a branch of artificial intelligence we use natural language processing everyday in translations and voice recognition.
Buy Now Pay Later.
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) is a method of payment that allows customers to order whatever they want and pay
either within 15 days or so from purchase or to pay in three (3) or more instalments.
The history of Buy Now Pay Later comes from Germany, where the payment on invoice, which allows german customers to order several products without paying anything upfront, choose the products you want to pay for after you receive them at home and then return the products that you don’t want, then the customer receives an invoice to pay just for the items he/she decided to keep is a consolidated practice in Germany.
When fashion e-commerce started off in Germany, this form of payment was very popular and it’s actually an enabler of conversion rate improvements.
So, it’s kind of a mandatory form of payment in certain markets.
Now, this type of payment has developed into different forms of payments. The pay by instalments with credit cards was initially a service offered by credit card, for example, in Japan, Then other payment providers like Scala Pay developed their own solution. And It’s becoming more and more popular among consumers.
And in Europe, More recently also PayPal has started its offer of pay by instalments. So now all the merchants who have PayPal installed can offer the pay by instalments with PayPal, without activating other payment providers.
In conclusion, Pay By Instalments or other forms of Buy Now and Pay Later are on our list of the key features to focus your roadmap on for fashion ecommerce in 2023. So keep an eye on them.
Headless commerce
What is headless commerce? Headless Commerce is a technology.
It’s a fairly recent way of building websites that allow e-tailers and brands to build websites that are fast and very flexible, in terms of web design capabilities. We already know about responsive design, site accelerators and content distribution networks, but this is something new, something different.
How endless commerce works, basically, breaking down the website into several components. So each component can be delivered separately and used differently according to where we want to display our website.
So instead of having a single platform for e-commerce that does everything in one single application. You have several components that you put together where and when you need them.
So, how headless commerce makes websites fast?
Headless commerce technology also called composable or jamstack, allows you to create static pages, Like HTML CSS, and images That can be distributed all over the world through a network of servers. So if you are in Japan, you can download your web page from a server based in Tokyo, rather than a server-based in New York. So the time it takes for your browser to load the page on your screen it’s shorter, and the time for you to start navigating on the website it’s less.
We know that we can achieve a similar result by introducing a content delivery network In our architecture. Even if we use another type of architecture, like a monolithic platform solution, like Magento, Shopify or Salesforce Commerce Cloud. They all leverage the capabilities of content delivery networks. However, all the users connected from all over the world are all requesting information from a single source or maybe two or more servers connected to each other by a load balancer.
In the headless architecture you have different applications doing different pieces of work. And the content is generally saved on edge servers near the users. While the transactional data like the price, the stock availability, and the checkout are delivered by a different application. That does only that specific job very fast.
In this way, we manage to leverage the distributed network of servers and we improve the speed of loading of our web pages, which we know is critical for the user experience and also for Google to rank on the search engines page results.
4) First party data and the end of Third party data
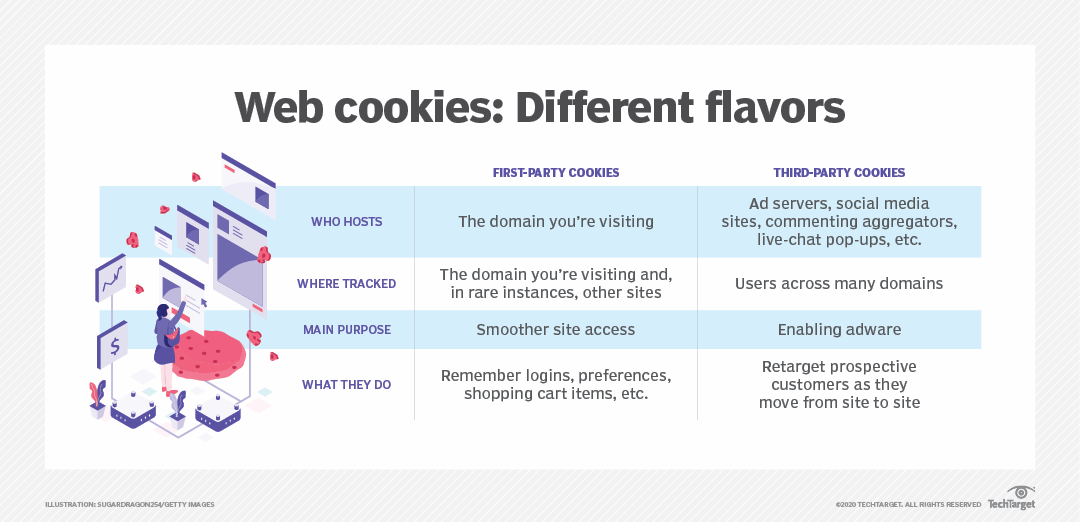
What are third party cookies? Third-party cookies are small text files that are placed on a user’s device by a domain that is different from the one the user is visiting. They are created by a third-party domain (i.e., a domain other than the one that the user is currently visiting), which is typically a company that provides some kind of service or content to the website that the user is visiting. Third-party cookies are commonly used for advertising and tracking purposes, and they can be used to collect information about a user’s browsing behavior, interests, and preferences.
Some examples:
- You are a leather goods brand and you want to target Prada users: with third party cookies you could advertise to people who have visited prada website
- You visit a shoe brand website and then you go to an online newspaper. When you browse the online newspaper you see the advertising of the shoes brand that you browsed before. This is possible because of third party cookies, i.e. the newspaper is using the cookie from the shoes brand that you have visited before to identify you. This is technically implemented by associating your brand website to an advertising network.